노드 N의 형식
- <LP, <K, A>, RP>
- K : 데이터 레코드의 키 값
- A : 키 값으로 K를 가진 데이터 레코드가 저장된 위치에 대한 포인터
- LP, RP : 좌/우측 서브트리에 대한 포인터
class Node{
Integer key;
Integer height;
Node llink;
Node rlink;
public Node(Integer key, Integer height, Node llink, Node rlink){
this.key = key;
this.height = height;
this.llink = llink;
this.rlink = rlink;
}
public Node(){
this(null, 0, null, null);
}
}이원 탐색 트리 T의 정의
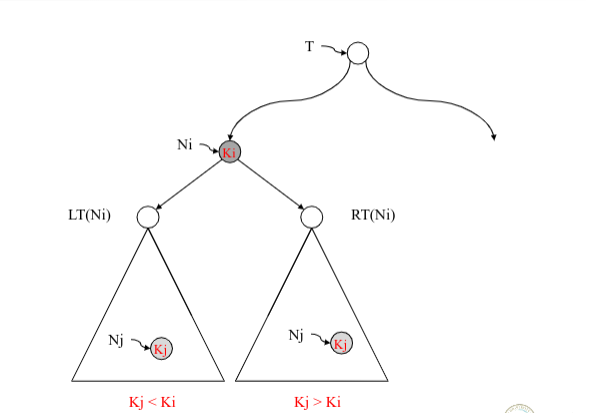
- T는 이진 트리(binary tree)이다.
- T의 모든 노드 N에 대해
- N의 왼쪽 서브 트리에 속하는 모든 키 값은 N의 키 값보다 작다.
- N의 오른쪽 서브 트리에 속하는 모든 키 값은 N의 키 값보다 크다.
=> 결과적으로 T의 모든 노드 N은 상이한 키 값을 가지며, 노드 N의 양쪽 서브 트리도 모두 BST이다.
BST 검색 (임의 접근) 알고리즘
// 스택에 상위 노드를 저장하는 동안 새 키를 삽입할 위치 찾기
while (p != null) {
if (newKey == p.key){
System.out.println(String.format("i %d : The key already exist", newKey));
return;
}
q = p;
stack.add(q);
if (newKey < p.key){
p = p.llink;
} else{
p = p.rlink;
}
}1. 트리가 공백 : 검색은 노드를 찾지 못하고 실패
2. K=Ki : 노드 Ni가 원하는 노드
3. K<Ki : Ni의 왼쪽 서브트리를 검색
4. K>Ki : Ni의 오른쪽 서브트리를 검색
BST 삽입 알고리즘
public void insertBST(int newKey){
Node p = this.root;
Node q = null;
Deque<Node> stack = new LinkedList<Node>();
// 스택에 상위 노드를 저장하는 동안 새 키를 삽입할 위치 찾기
while (p != null) {
if (newKey == p.key){
System.out.println(String.format("i %d : The key already exist", newKey));
return;
}
q = p;
stack.add(q);
if (newKey < p.key){
p = p.llink;
} else{
p = p.rlink;
}
}
// 새 노드 생성
Node newNode = getNode();
newNode.key = newKey;
// q의 자식으로 newNode 삽입
if (this.root == null){
this.root = newNode;
} else if (newKey < q.key){
q.llink = newNode;
} else {
q.rlink = newNode;
}
// 스택에서 상위 노드의 높이 업데이트
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
q = stack.pop();
int val;
if ((q.llink == null) && (q.rlink == null)){
continue;
} else if (q.rlink == null) {
q.height = q.llink.height + 1;
} else if (q.llink == null) {
q.height = q.rlink.height + 1;
} else {
val = (q.llink.height < q.rlink.height) ? q.rlink.height : q.llink.height;
q.height = 1 + val;
}
}
}1. 트리가 공백 : K를 루트 노드로 삽입
2. K=Ki : 트리에 값은 키 값이 존재하므로 삽입을 거부
3. K<Ki : Ni의 왼쪽 서브트리로 이동하여 삽입
4. K>Ki : Ni의 오른쪽 서브트리로 이동하여 삽입
BST 삭제 알고리즘
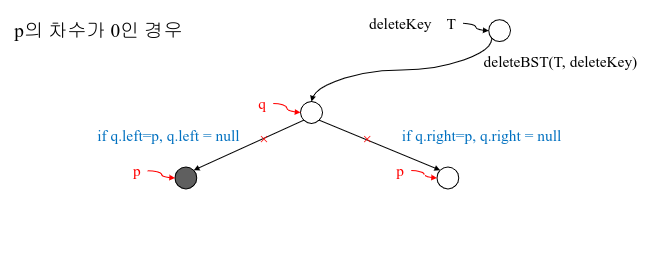
1. 자식이 없는 리프 노드(차수가 0인 노드)의 삭제
=> 단순히 그 노드를 삭제
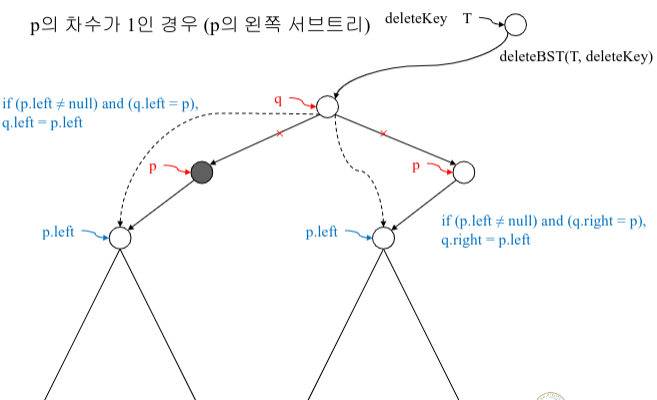
2. 자식이 하나인 노드(차수가 1인 노드)의 삭제
=> 삭제되는 노드 자리에 자식 노드를 위치
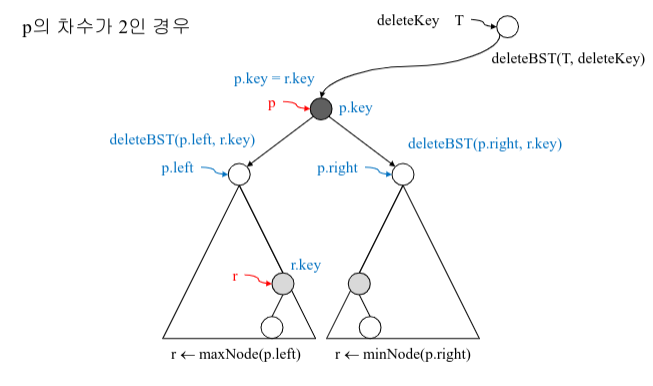
3. 자식이 둘인 노드(차수가 2인 노드)의 삭제
=> 삭제할 노드를 왼쪽 서브트리에서 제일 큰 키 값 또는 오른쪽 서브트리에서 제일 작은 키 값으로 대체.
(두 경우 중 높이가 높은 서브트리를 선택하는 것이 유리, 즉 균형 트리 유지)
public void deleteBST(int deletekey){
Node p = this.root;
Node q = null;
Deque<Node> stack = new LinkedList<Node>();
// 스택에 상위 노드를 저장하는 동안 deleteKey 위치 찾기
while ((p != null) && (deletekey != p.key)){
q = p;
stack.add(q);
if (deletekey < p.key){
p = p.llink;
} else {
p = p.rlink;
}
}
if (p == null) {
System.out.println(String.format("d %d : The key does not exist", deletekey));
return;
}
// 자식수가 2의 경우는 0의 경우 또는 1의 경우로 축소된다.
if (p.llink != null && p.rlink != null) {
stack.add(p);
Node temp = p;
if (height(p.llink) < height(p.rlink)){
// minNode
p = minNode(p.rlink, stack);
} else if (height(p.llink) > height(p.rlink)){
// maxNode
p = maxNode(p.llink, stack);
} else {
// System.out.println(noNodes(p.llink) + " " + noNodes(p.rlink));
if (noNodes(p.llink) >= noNodes(p.rlink)){
p = maxNode(p.llink, stack);
} else {
p = minNode(p.rlink, stack);
}
}
temp.key = p.key;
q = stack.getLast();
}
// 이제 p의 도수는 0 또는 1이다.
// T에서 p를 삭제하다
if (p.llink == null && p.rlink == null) {
if (q == null) {
this.root = null;
} else if (q.llink == p){
q.llink = null;
} else {
q.rlink = null;
}
// case of degree 1
} else {
if (p.llink != null) {
if (q == null) {
this.root = this.root.llink;
} else if (q.llink == p) {
q.llink = p.llink;
} else {
q.rlink = p.llink;
}
} else {
if (q == null) {
this.root = this.root.rlink;
} else if (q.llink == p) {
q.llink = p.rlink;
} else {
q.rlink = p.rlink;
}
}
}
p = null;
// 스택에서 상위 노드를 pop 하면서 높이 업데이트
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
q = stack.pop();
int val;
if ((q.llink == null) && (q.rlink == null)){
continue;
} else if (q.rlink == null) {
q.height = q.llink.height + 1;
} else if (q.llink == null) {
q.height = q.rlink.height + 1;
} else {
val = (q.llink.height < q.rlink.height) ? q.rlink.height : q.llink.height;
q.height = 1 + val;
}
}
}BST 성능
편향 이원 탐색 트리(skewed BST)
– 리프 노드의 탐색 시간은 최악
– 노드 개수가 N개인 이원 탐색 트리에서 최악의 탐색 시간 : N번의 노드 탐색
N개의 노드를 갖는 높이 h인 BST의 최소 높이
– N <= 2h – 1
– N + 1 <= 2h
– [log2(N+1)] <= h
BST의 최소/최대 높이
– [log2(N+1)] <= h <= N
Best case : Complete binary tree
Worst case : Skewed binary tree
BST 성능 개선
이원 탐색 트리의 특징 (단점)
– 삽입, 삭제 후 효율적 접근을 위한 균형 유지 부담
– 작은 분기율(branching factor)에 따른 긴 탐색 경로와 검색 시간
(분기율=2 이므로, 각 노드는 많아야 두 개의 서브트리)
성능 개선 방향
– 균형 트리(balanced tree)
모든 노드에 대해, 양쪽 서브트리의 높이가 가능한 같게 만들어, 트리의 최대 경로 길이를 최소화.
즉, 삽입 그리고 삭제 후에는 트리가 균형을 유지하도록 트리를 재구성(restructuring)
– 재구성 시간의 부담으로, 완벽한 균형 트리는 유지 불가능함.
전체 코드
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
class Node{
Integer key;
Integer height;
Node llink;
Node rlink;
public Node(Integer key, Integer height, Node llink, Node rlink){
this.key = key;
this.height = height;
this.llink = llink;
this.rlink = rlink;
}
public Node(){
this(null, 0, null, null);
}
}
public class BST{
Node root;
Deque<Integer> list;
Integer totalSub;
public BST(){
this.root = null;
}
public Node getNode(){
return new Node();
}
public void insertBST(int newKey){
Node p = this.root;
Node q = null;
Deque<Node> stack = new LinkedList<Node>();
// 스택에 상위 노드를 저장하는 동안 새 키를 삽입할 위치 찾기
while (p != null) {
if (newKey == p.key){
System.out.println(String.format("i %d : The key already exist", newKey));
return;
}
q = p;
stack.add(q);
if (newKey < p.key){
p = p.llink;
} else{
p = p.rlink;
}
}
// 새 노드 생성
Node newNode = getNode();
newNode.key = newKey;
// q의 자식으로 newNode 삽입
if (this.root == null){
this.root = newNode;
} else if (newKey < q.key){
q.llink = newNode;
} else {
q.rlink = newNode;
}
// 스택에서 상위 노드의 높이 업데이트
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
q = stack.pop();
int val;
if ((q.llink == null) && (q.rlink == null)){
continue;
} else if (q.rlink == null) {
q.height = q.llink.height + 1;
} else if (q.llink == null) {
q.height = q.rlink.height + 1;
} else {
val = (q.llink.height < q.rlink.height) ? q.rlink.height : q.llink.height;
q.height = 1 + val;
}
}
}
public int height(Node T){
return T.height;
}
public Node minNode(Node T, Deque<Node> stack){
while (T.llink != null){
stack.add(T);
T = T.llink;
}
return T;
}
public Node maxNode(Node T, Deque<Node> stack){
while (T.rlink != null){
stack.add(T);
T = T.rlink;
}
return T;
}
public int noNodes(Node T){
this.totalSub = 0;
dfs(T);
return this.totalSub;
}
public void deleteBST(int deletekey){
Node p = this.root;
Node q = null;
Deque<Node> stack = new LinkedList<Node>();
// 스택에 상위 노드를 저장하는 동안 deleteKey 위치 찾기
while ((p != null) && (deletekey != p.key)){
q = p;
stack.add(q);
if (deletekey < p.key){
p = p.llink;
} else {
p = p.rlink;
}
}
if (p == null) {
System.out.println(String.format("d %d : The key does not exist", deletekey));
return;
}
// 자식수가 2의 경우는 0의 경우 또는 1의 경우로 축소된다.
if (p.llink != null && p.rlink != null) {
stack.add(p);
Node temp = p;
if (height(p.llink) < height(p.rlink)){
// minNode
p = minNode(p.rlink, stack);
} else if (height(p.llink) > height(p.rlink)){
// maxNode
p = maxNode(p.llink, stack);
} else {
// System.out.println(noNodes(p.llink) + " " + noNodes(p.rlink));
if (noNodes(p.llink) >= noNodes(p.rlink)){
p = maxNode(p.llink, stack);
} else {
p = minNode(p.rlink, stack);
}
}
temp.key = p.key;
q = stack.getLast();
}
// 이제 p의 도수는 0 또는 1이다.
// T에서 p를 삭제하다
if (p.llink == null && p.rlink == null) {
if (q == null) {
this.root = null;
} else if (q.llink == p){
q.llink = null;
} else {
q.rlink = null;
}
// case of degree 1
} else {
if (p.llink != null) {
if (q == null) {
this.root = this.root.llink;
} else if (q.llink == p) {
q.llink = p.llink;
} else {
q.rlink = p.llink;
}
} else {
if (q == null) {
this.root = this.root.rlink;
} else if (q.llink == p) {
q.llink = p.rlink;
} else {
q.rlink = p.rlink;
}
}
}
p = null;
// 스택에서 상위 노드를 pop 하면서 높이 업데이트
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
q = stack.pop();
int val;
if ((q.llink == null) && (q.rlink == null)){
continue;
} else if (q.rlink == null) {
q.height = q.llink.height + 1;
} else if (q.llink == null) {
q.height = q.rlink.height + 1;
} else {
val = (q.llink.height < q.rlink.height) ? q.rlink.height : q.llink.height;
q.height = 1 + val;
}
}
}
public void inorderBST(Node head){
this.list = new LinkedList<Integer>();
inorder(head);
for (int key : list) {
System.out.print(key + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public void inorder(Node travel){
if (travel != null){
if (travel.llink != null) {
inorder(travel.llink);
}
this.list.add(travel.key);
if (travel.rlink != null) {
inorder(travel.rlink);
}
}
}
public void dfs(Node sub_root){
if (sub_root == null){
return;
}
dfs(sub_root.llink);
this.totalSub += 1;
dfs(sub_root.rlink);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
BST tree = new BST();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i=0; i<30; i++){
int val = random.nextInt(1000);
while (list.contains(val)){
val = random.nextInt(1000);
}
tree.insertBST(val);
list.add(val);
tree.inorderBST(tree.root);
}
for (int i=0; i<30; i++){
int idx = random.nextInt(list.size());
tree.deleteBST(list.get(idx));
list.remove(idx);
tree.inorderBST(tree.root);
}
}
}